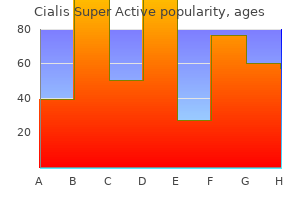
"Buy cialis super active 20mg free shipping, erectile dysfunction middle age".
By: Z. Basir, M.S., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Meharry Medical College School of Medicine
However erectile dysfunction treatment comparison cialis super active 20mg on-line, the diagnosis of myelodysplasia requires microscopic examination of bone marrow cell morphology erectile dysfunction lifestyle changes discount cialis super active online master card, and diagnosis of sideroblastic anemia (Color Plate 6 E) also requires Prussian blue staining (for detection of iron) of normoblasts in the bone marrow (Table 159-6) impotence natural remedy generic cialis super active 20mg line. If there is mild microcytic anemia with significant numbers of target cells, thalassemia trait is the most likely diagnosis. A patient with a rheumatologic or lymphoproliferative disease may have anemia of chronic disease but then may have a marked change in the severity of the anemia because of the development of autoimmune hemolysis. A patient with chronic hemolytic anemia such as sickle cell disease, thalassemia, or hereditary spherocytosis may develop folate deficiency or become infected with parvovirus B19, which prevents the bone marrow from continuing to overproduce erythrocytes and leads to a marked increase in the severity of the anemia. Excellent summaries of practical approaches to the evaluation and management of anemias. Young Blood cell counts may be low because cells are prematurely removed from the peripheral circulation or are inadequately produced in the bone marrow. Bone marrow failure is often classified by other dominant clinical or morphologic features. The term bone marrow failure is vague and inclusive, and it awaits redefinition with more precise understanding of pathophysiologic processes. By default, therefore, the disorders of bone marrow failure are currently defined by their marrow pathology: the fatty bone marrow of aplastic anemia, the disordered hematopoiesis of the myelodysplasias, and the fibrosis of myelofibrosis. Making inferences about disease processes from the appearance of the bone marrow is as misleading as it is inevitable; what is understood must be distinguished from what is conjecture. Aplastic anemia is a disease of the young, with a median age at onset of about 25 years (excluding aplasia secondary to cancer chemotherapy). It is the most common cause of pancytopenia in the adolescent or young adult (Fig. The commonly accepted definition for severe disease is two of the following: (1) absolute neutrophil count (percentage of polymorphonuclear and band forms multiplied by the total white blood cell count) of less than 500/mm3; (2) platelets less than 20,000/mm3; and (3) anemia with a reticulocyte count (corrected for hematocrit) less than 1% (or an absolute reticulocyte count less than 40,000/mm3). A subset of very severe aplastic anemia, with the worst prognosis, is defined by more severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count less than 200/mm3). Some patients have bone marrow hypocellularity and depression of only two of the three major blood lines; many such cases progress to typical aplastic anemia. Failure of a single lineage also occurs in pure red cell aplasia (rare), megakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (extremely rare), and agranulocytosis (not rare but usually an idiosyncratic drug reaction). These syndromes show the characteristic absence of a single set of recognizable precursor cells in otherwise cellular bone marrow, and in this way they are differentiated from the much more common causes of anemia. The pathophysiology of the more restricted marrow failure states is probably similar to that of general bone marrow failure, but with a more mature target cell. Fanconi described children with inherited pancytopenia and hypocellular marrows and with associated anomalies of the skeletal and urogenital systems. Congenital pure red cell aplasia (Diamond-Blackfan syndrome) lacks a cytogenetic marker or associated physical abnormalities. Isolated neutropenia or thrombocytopenia occurs in a number of pediatric syndromes. Etiology In the majority of patients, aplastic anemia is diagnosed as "idiopathic. Nuclear accidents and radiation injury can involve not only power plant workers but also employees of hospitals, laboratories, and industry. Myelodysplasia and leukemia, but not aplastic anemia, are late effects of irradiation. Benzene has been clearly linked to bone marrow failure, but the quality of the case reports, many from the early part of the century, usually does not allow accurate discrimination between aplasia and myelodysplasia (benzene exposure also increases the risk of acute leukemia). The occurrence of hematologic abnormalities is roughly correlated with cumulative exposure, but there must also be an important element of susceptibility, because only a minority of even heavily exposed workers develop evidence of myelotoxicity. A history of past employment is important, especially in "open" industries in which benzene is used for a secondary purpose (usually as a solvent) rather than in "closed" industries for chemical production. Benzene-related blood diseases have declined with regulation of industrial exposure, and benzene is not generally available as a household solvent. The association of marrow failure with other organic chemicals is much less well substantiated. Many of the common cancer chemotherapeutic drugs regularly and predictably suppress the bone marrow. A large and diverse group of other drugs have been linked to idiosyncratic aplastic anemia (see Table 26-5), but some of these associations are based on case reports and are tenuous at best. For example, some incriminated drugs may have been used to treat the first symptoms of bone marrow failure (antibiotics for fever or the preceding viral illness) or may have provoked the first symptom of a pre-existing disease (petechiae produced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents administered to a thrombocytopenic individual).
This "microalbuminuria" precedes the later development of larger rates of albumin excretion detectable by standard dipstick technology or other chemical assays erectile dysfunction pills south africa generic cialis super active 20 mg amex. The lag time between the appearance of microalbuminuria and full-blown proteinuria is typically in the range of 1 to erectile dysfunction low libido order cialis super active 20mg visa 5 years erectile dysfunction doctors in charleston sc buy cialis super active 20mg with amex. However, recent advances in therapy seem likely to prolong this interval, forestalling the appearance of the more overt phases of the disease (see later). Without effective treatment (see later), the albuminuria tends to progressively worsen, and arterial hypertension usually supervenes in this subgroup during the transition between microalbuminuria and greater degrees of proteinuria. Thus, from the first evidence of standard dipstick-positive proteinuria and numerically only modest elevations of serum creatinine above the normal range, the time to end-stage renal disease has been 3 to 8 years. However, during this interval, arterial hypertension is prevalent, if asymptomatic, and protein excretion rates can rise to the levels of a nephrotic syndrome with the usual clinical and biochemical consequences of edema, hypoalbuminemia, and hypercholesterolemia. When the decay in filtration rate reaches the last 10 to 30% of baseline levels, uremic symptoms begin to appear. However, as with other progressive renal diseases, considerable individual variability exists in the development and severity of uremic symptoms. Furthermore, several elements of diabetes and its complications may exacerbate uremic symptoms or be indistinguishable from them. The nausea and vomiting that mark the uremic phase may be complicated by diabetic autonomic neuropathy with poor gastric emptying due to gastroparesis. Distinguishing between gastroparesis and uremic nausea and vomiting is often difficult. Furthermore, diabetic peripheral neuropathy in its sensory disturbance may to some degree mimic uremic neuropathy, although in general the painful and hypesthetic neuropathic symptoms are more attributable to long-standing diabetes than to uremia in most patients. The presence of autonomic neuropathy also may make it harder to manage arterial hypertension in some patients. Specifically, the propensity to orthostatic hypotension with certain drugs may be exaggerated in the presence of autonomic neuropathy; and for some patients, their arterial pressure may be quite elevated when supine but below normal when standing. However, for both categories of diabetes, myocardial infarction, stroke, and progressive peripheral vascular disease often requiring amputation seem to occur disproportionately in diabetic patients with renal failure compared with those spared from kidney disease. The heightened filtration and an enlarged overall renal size of early diabetes are matched by increases in glomerular and tubular size. With microalbuminuria and yet greater degrees of proteinuria and hypertension, the more characteristic glomerular changes become ever more prominent (Fig. Increases in the mesangial compartment of the glomerulus are produced by increases in matrix and probably in the number of mesangial cells. These expansions can manifest as diffuse enlargement of this portion of the glomerulus as well as nodular increases in extracellular matrix material. These latter lesions have been termed Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules but probably represent simply a different geometric arrangement of the generalized mesangial expansion. As the mesangium expands, the density of capillaries and their area for filtration progressively decline, and these abnormalities are thought to play an important role in the falling filtration rate. The glomerular basement membrane also progressively thickens, although this change Figure 110-2 Electron photomicrograph of a portion of a glomerulus from a patient with proteinuric, diabetic glomerulopathy (magnification Ч5000). A striking increase in collagenous components has resulted in (1) widening of the basement membrane of peripheral capillary loops (small arrows) and (2) expansion of the matrix of the glomerular mesangium (large arrows). The latter alteration is responsible for compressing and ultimately obliterating the glomerular capillary network. Hyaline-like material (a presumed protein of uncertain type) can deposit in the arterioles about the glomerulus as well as in droplets along the capillary loops themselves. As with most progressive renal diseases, a prominent tubulointerstitial pathology develops pari passu with the glomerular abnormalities. The tubular basement membranes thicken, and occasional glycogen droplets appear in tubular epithelium. However, these tubulointerstitial abnormalities have few particular diagnostic features for diabetes but may be important in occluding vascular and tubular structures and contributing to the demise of renal function. In the main, the tubulointerstitial lesions comprise progressive fibrosis and mononuclear cell infiltrates surrounding atrophic tubules, some containing proteinaceous casts. However, roughly similar patterns of nodular expansion can develop in the glomerulus in non-diabetic renal disease.
The stiff-person syndrome is characterized by rigidity and spasms of muscles associated with antiamphiphysin antibodies and breast cancer free erectile dysfunction drugs buy cialis super active in india. Most "stiff persons" do not have cancer erectile dysfunction early age buy cialis super active australia, but they produce antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase that cause both diabetes and the neurologic disorder erectile dysfunction treatment calgary cialis super active 20 mg sale. Peripheral Nerves and Dorsal Root Ganglia Four clinical peripheral nerve disorders occur in association with cancer. Characteristic of carcinoma is subacute sensory neuronopathy marked by loss of sensation with relative preservation of motor power. The illness usually precedes appearance of the carcinoma and progresses over a few months, and the patient is left with moderate or severe disability. Pathologically, destruction of posterior root ganglia with perivascular lymphocytic cuffing and wallerian degeneration of sensory nerves is noted. Many patients also have encephalomyelitis with inflammatory and degenerative changes in the brain and spinal cord. The disorder, when associated with small cell carcinoma, is characterized by anti-Hu antibodies. More common than sensory neuronopathy is a distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy characterized by motor weakness, sensory loss, and absence of distal reflexes in the extremities. The illness is pathologically characterized by either segmental demyelination or axonal degeneration (or both) of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. Pathologically and clinically, the sensorimotor neuropathy is indistinguishable from polyneuropathies not associated with cancer. Indeed, some have suggested that late or terminal polyneuropathy may be due to nutritional deprivation associated with cancer. Its etiology, however, is not clear, and it does not respond to treatment with vitamins or other nutritional supplements. A few patients with neuropathy limited to the autonomic nervous system have been reported. Myasthenia gravis is associated with thymomas but not usually with other systemic tumors. The Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome is characterized by weakness and fatigability of proximal muscles, particularly of the pelvic girdle and thighs. Patients often complain of dryness of the mouth, impotence, pain in the thighs, and peripheral paresthesias. Proximal muscles are weak, but strength increases over several seconds of 1053 sustained contraction. The diagnosis is made by electromyographic studies in which repeated nerve stimulation at rates above 10 per second causes a progressive increase in the size of the muscle action potential (the opposite of myasthenia gravis). About two thirds of patients with this syndrome either have cancer or will develop cancer, usually small cell carcinoma of the lung. Most patients harbor P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channel antibodies in their serum, an excellent diagnostic test. Plasmapheresis and immunosuppressant drugs usually relieve the symptoms, as may successful treatment of the neoplasm. The illness responds poorly to anticholinesterase drugs but does respond to 3,4-diaminopyridine in doses up to 100 mg/day. Typical dermatomyositis or polymyositis may occur as a remote effect of cancer (see Chapter 296). Fewer than 10% of patients with this disorder have cancer, but the figure is higher in older patients. Pathologically, it is possible to differentiate two groups: one with the typical inflammatory lesions of polymyositis and one with little inflammation but severe muscle necrosis. These patients respond less well to corticosteroid therapy than do those with dermatomyositis unaccompanied by cancer, although substantial improvement with steroid treatment sometimes occurs. Some patients with cancer complain of weakness and fatigability that seem worse than can be accounted for by their cancer alone.
Buy cialis super active canada. How YOGA Can Cure Erectile Dysfunction? You Will Lose Your Mind About The Way Yoga Works..
Such physiologic effects are not observed at more conventional levels of intake and are therefore usually considered to erectile dysfunction drugs for diabetes order cialis super active 20mg mastercard be "pharmacologic" effects of the nutrient erectile dysfunction drugs wiki order cialis super active from india. Its primary function in humans is to erectile dysfunction statistics nih generic cialis super active 20 mg without a prescription potentiate insulin action, which it accomplishes as a circulating dinicotinoglutathione complex called glucose tolerance factor. Elevated plasma free fatty acid concentration, neuropathy, encephalopathy, and abnormalities in nitrogen metabolism are also reported. Whether supplemental chromium may improve glucose tolerance in mildly glucose-intolerant but otherwise healthy individuals remains controversial. Clinical manifestations include depigmentation of skin and hair, neurologic disturbances, leukopenia, hypochromic microcytic anemia, and skeletal abnormalities. The anemia arises from impaired utilization of iron and is therefore a conditioned form of iron deficiency anemia. Toxicity Toxicity after oral ingestion is uncommon and seems confined to gastric irritation. Airborne exposure may cause contact dermatitis, eczema, skin ulcers, and bronchogenic carcinoma. Assessment of Status Plasma or serum concentrations of chromium are crude indicators of chromium status; they appear to be meaningful when their value is markedly above or below the normal range. It is carried to the liver, where it is bound to ceruloplasmin, which circulates systematically and delivers copper to target tissues in the body. Absorptive and excretory processes vary with the levels of dietary copper and thereby provide a means of copper homeostasis. Copper serves as a component of many enzymes, including amine oxidases, ferroxidases, cytochrome- c oxidase, dopamine beta-hydroxylase, superoxide dismutase, and tyrosinase. Acute copper toxicity has been described after excessive oral intake and with absorption of copper salts applied to burned skin. Milder manifestations include nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, and diarrhea; coma and hepatic necrosis may ensue in severe cases. Wilson disease is a rare, inherited disease associated with abnormally low ceruloplasmin levels and accumulation of copper in the liver and brain, eventually leading to damage to these two organs (see Chapter 120). Large doses (>2 mg/d in adults) may induce hypothyroidism by blocking thyroid hormone synthesis. Supplementation with >100 mug/day to an individual who was formerly deficient occasionally induces hyperthyroidism. Marked deficiency is reliably detected by diminished serum copper and ceruloplasmin concentrations, as well as by low erythrocyte superoxide dismutase activity. It is incorporated into the crystalline structure of bone, thereby altering its physical characteristics. Estimates of intake or clinical assessment are used because no good laboratory test exists. Iodine Readily absorbed from the diet, concentrated in the thyroid, and integrated into the thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. They modulate resting energy expenditure and, in the developing human, growth and development. In the absence of supplementation, populations relying primarily on food from soil with a low iodine content have endemic iodine deficiency. Maternal iodine deficiency leads to fetal deficiency, which produces spontaneous abortions, still-births, hypothyroidism, cretinism, and dwarfism. Permanent cognitive deficits may also be induced by iodine deficiency during infancy and childhood. In the adult, compensatory hypertrophy of the thyroid (goiter) occurs along with varying degrees of hypothyroidism. Women of childbearing age constitute the highest-risk group because of menstrual blood loss, pregnancy, and lactation. In children, mild deficiency insufficient to cause anemia is associated with behavioral disturbances and poor school performance. The thyroid-stimulating hormone level in the blood is an indirect and therefore not entirely specific means of assessment. Iron Participates in redox reactions in a number of metalloproteins such as hemoglobin, myoglobin, and the cytochrome enzymes.