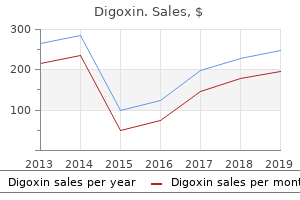
"Order 0.25mg digoxin fast delivery, blood pressure medication with the least side effects".
By: Q. Lares, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Figure 1: Phylogenetic classification and abundance (logarithmic scale) of microbial genes identified in faecal samples from European individuals arteria revista order digoxin 0.25 mg with amex. The vast majority of gene sequences belong to arteria umbilical unica pdf purchase discount digoxin on-line the domain Bacteria or cannot be classified (unknown) blood pressure xl cuff order cheap digoxin on-line. Each individual harbours his or her own distinctive pattern of gut microbial communities. Bacterial composition in the lumen varies from caecum to rectum, and faecal samples may not reproduce luminal contents in proximal segments of the gastrointestinal tract. In contrast, the community of mucosa-associated bacteria is highly stable from terminal ileum to the large bowel in a given individual. However, stool samples are widely accepted as the best approach for investigating gut microbial communities due to their accessibility for multiple sampling over time; they should be viewed as a proxy for other, less accessible, anatomic sites. Factors such as diet, drug intake, travelling or simply colonic transit time, have an impact on microbial composition in faecal samples over time in a unique host. There are striking differences in composition and diversity between westernized and non-westernized populations. Microbial diversity changes with age, but the faecal microbiota of adults is less diverse in metropolitan areas of North America than in rural non-westernized populations of Africa and South America. The basis for the enterotype clustering is unknown but appears independent of nationality, sex, age, or body mass index. As shown in Figure 2, the three enterotype partitioning is also present in Chinese population. Dysbiosis Pathologies such as inflammatory bowel diseases, obesity, type 2 diabetes, irritable bowel syndrome, Clostridium difficile-associated disease, and others, have been linked to changes in the composition of the gut microbiota referred to as dysbiosis. Consistency among studies is still poor for some of these examples, possibly because of lack of fully standardized methodology. In addition, such associations do not necessarily indicate a causative role for the microbiota in the pathogenesis of a disease, as they could rather be a consequence of the disease. Follow-up studies and, particularly, intervention studies aimed at restoring the normal composition of the gut microbiota are needed. Full metagenomic investigation of faecal samples by whole genome sequencing, termed quantitative metagenomics, is an accurate and unparalleled approach to investigate microbial diversity in the human gut. This strategy can assess the presence and abundance of genes from known as well as unknown taxa, including not only bacteria but also virus and eukaryotes (yeasts, protists). Using this methodology, it has been shown that a high proportion of Europeans (23%) exhibit microbial gene counts below the median of 600. Microbial gene counts can be used as an accurate biomarker of microbial diversity or richness of the gut ecosystem. Moreover, these metabolic parameters were found to be slightly altered even in otherwise healthy individuals with low microbial gene counts. Obese individuals with low gene counts gain more weight over time and have a propensity towards a malignant form of obesity. Low gene richness thus appears to be a risk factor for development of metabolic syndrome related complications, such type 2 diabetes, hepatic and cardiovascular pathologies. A few bacterial species are sufficient to distinguish between individuals with high and low microbial richness and thus easily identify individuals at risk. From a functional point of view, low diversity is associated with a reduction in butyrate-producing bacteria, increased mucus degradation potential, reduced hydrogen and methane production potential combined with increased hydrogen sulphide formation potential, and increased potential to manage oxidative stress. Importantly, a nutritional intervention led to the improvement of gene richness, offering hope for restoration of the healthy microbiome and thus alleviation of the risk to develop certain chronic diseases. In conclusion, richness of the gut microbial ecosystem appears to be a critical characteristic for a healthy gut microbiota. Full metagenomic analysis of faecal samples from a cohort of European adult subjects identified a total of 3. Each individual carries an average of 600, 000 non-redundant microbial genes in the gastrointestinal tract (Table 1), and around 300, 000 microbial genes are common in the sense that they are present in about 50% of individuals. Interestingly, Bacteroides, Faecalibacterium and Bifidobacterium are the most abundant genera but their relative proportion is highly variable across individuals. Enterotypes Network analysis of species abundance across different individuals suggested that the human microbiome comprises well balanced hostmicrobial symbiotic states driven by groups of co-occurring species and genera.

Finally arrhythmia hereditary order 0.25mg digoxin with mastercard, complementing the employed workforce Copyright National Academy of Sciences blood pressure medication lack of energy buy cheap digoxin 0.25mg line. Again arteria vitellina cheap digoxin 0.25mg visa, there is little information available about the size, nature, preparation, and functioning of this important sector of the health care workforce. This mix of different disciplines and licensed, unlicensed, and informal caregivers contributes to the difficulty of determining whether the number of workers is adequate to provide psychosocial health services. Ideally, one might want to estimate carefully the level of need for these services and then attempt to predict accurately the necessary workforce supply to meet that need. Even in countries with centrally managed, universal health care systems, progress in medical technology and changes in the organization of care can create large forecasting errors. Predicting workforce supply in the United States is further complicated by the fact that demand for services is not tightly controlled, and the distribution of the workforce is neither controlled nor actively shaped through reimbursement mechanisms (Reinhardt, 2002). To complicate the matter, data on health professions are not collected in a routine, standardized fashion across the multiple disciplines (Hoge et al. Thus, workforce needs are heavily influenced at the local level by the assignment of functions to providers. For these and other reasons discussed in Appendix B, the development of estimates of the overall workforce capacity required to meet psychosocial health needs through modeling or other methods was not a feasible activity for this study. Nonetheless, shortages and maldistribution of a variety of psychosocial health care providers, such as nurses and mental health clinicians is a long-recognized problem. And the American Association of Medical Colleges estimates that the growing need for cancer care will soon outstrip the supply of oncologists, and predicts a shortage by 2020 (Erikson et al. As described in previous chapters, this ability is influenced in part by how work in clinical practices is designed (Chapters 4 and 5) and how incentives from payers and oversight organizations operate (Chapter 6). Although most professions have developed educational standards addressing psychosocial issues, it is unclear how these standards have been translated into educational curricula and more important, whether they create the competencies needed in the health care workforce to meet psychosocial health needs effectively. Professional education should prepare licensed clinicians to recognize and address psychosocial health needs just as they do biomedical needs. The education of mental health and social service professionals should Copyright National Academy of Sciences. While the biopsychosocial model of health care has long been advocated (Engel, 1977), the extent to which this model is adequately implemented in educational curricula is unclear. Licensing and continuing education requirements and credentialing standards pertaining to psychosocial factors also are unclear and appear to be limited, with variations across professions. This lack of data impedes the ability to reach conclusions about the current state and adequacy of behavioral and social science instruction in U. It [the curriculum] must include current concepts in the basic and clinical sciences, including therapy and technology, changes in the understanding of disease, and the effect of social needs and demands on care. The curriculum must include behavioral and socioeconomic subjects, in addition to basic science and clinical disciplines. Clinical instruction must cover all organ systems, and include the important aspects of preventive, acute, chronic, continuing, rehabilitative, and end-of-life care. There must be specific instruction in communication skills as they relate to physician responsibilities, including communication with patients, families, colleagues, and other health professionals [emphasis added]. About 50 percent of medical schools endorsed less than 40 hours of total instruction in psychosomatic/ behavioral medicine out of the 7, 0008, 000 hours in the average medical school curriculum. The researchers concluded that the degree of coverage of the subject in undergraduate medical education appeared variable, but generally was unknown and difficult to assess (Waldstein et al. Further, medical schools that participate have flexibility in data entry, and as a result, the data submitted vary in detail from school to school. Medical Licensure To practice legally as a physician, medical students must pass the three-step U. Step 1 of the exam (usually taken after the second year in medical school) assesses basic science knowledge according to general principles and individual organ systems. Box 7-2 shows the subtopics in the Step 1 exam that address psychosocial communication, M. However, such test questions would most likely be woven together with questions dealing with chronic diseases instead of making up a separate section devoted to psychological and social factors. It tests clinical knowledge and communication and interpersonal skills using standardized patients.
The blood which is vomited is either bright red or dark with the consistency of coffee grounds arteria glutea superior buy generic digoxin 0.25 mg on-line. Bleeding near the anus (for example hypertension va compensation order digoxin toronto, hemorrhoids) is bright red mixed with the stool blood pressure tracking chart cheap digoxin 0.25mg with amex. A person suffering from a massive hemorrhage will exhibit these signs and symptoms with a rapid decrease in body blood volume go into profound shock. Pale skin, thirst, faintness, sweating, and eventually collapse also characterize massive hemorrhage. This patient needs blood transfusions, intravenous feedings, and rest until the bleeding has stopped. Erosion of an ulcer through the wall of an organ (for example, the stomach) is called perforation. The patient experiences sudden, severe pain which is located in the middle portion of the stomach. If these symptoms are severe enough, the patient may faint but regain consciousness quickly when placed in the recumbent position (lying down). The pain may radiate to the shoulders and the right lower quadrant of the abdomen then lessen for a few hours. When palpated, the abdomen is found to be tender, abdominal muscles are rigid, and bowel sounds are quieter than normal. The patient usually lies as still as possible in an effort to avoid any movement which will increase the pain. If surgery is delayed more than 24 hours, begin gastric suction, antibiotics, and intravenous fluids. This complication is the extension of the ulcer crater beyond the duodenal wall into the adjacent organs. The penetration actually extends into the deep tissues of an organ; for example, a duodenal ulcer may penetrate into the pancreas or liver. Symptoms include intense pain which is persistent and which may occur in the back. The pain is more intense at night, and the patient gets no relief from eating food or taking antacids. A patient with a long history of duodenal ulcer who suddenly experiences these symptoms will usually have an ulcer complicated by penetration. When treatment by antacids is unsuccessful in producing healing, surgery is necessary. Obstruction as an ulcer complication refers to the blocking or clogging of the gastrointestinal tract. There are two types of pyloric obstruction due to ulcer: spastic obstruction and scar obstruction. Spastic obstruction is characterized by edema (swelling) underlying spasm of the pylorus (the opening between the stomach and duodenum through which stomach contents pass in the digestive process) and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). With proper treatment, patients with spastic obstruction can recover completely, or they may have repeated attacks fully recovering from each attack. Scar tissue has formed at the opening of the pylorus and duodenum causing that opening to become narrower. Because of these feelings, the patient may have limited his own food intake and lose weight as a result. The goal of medical treatment of peptic ulcer is to provide the best conditions for the ulcer to heal. To that end, treatment tries to increase the pH level and neutralize gastric hydrochloric acid as well as reduce the amount of hydrochloric acid secreted. If the patient must work, he should arrange for rest periods while at work and be sure to get enough sleep at night. The bland, smooth diets prescribed for ulcer patients in the past are not considered today to promote ulcer healing.
This medium therefore serves as a valuable exemplar for further study in how various mass media might influence the potential for tobacco use arteria networks corp discount 0.25 mg digoxin. Later sections examine research findings regarding exposure to blood pressure and dehydration purchase cheap digoxin on line tobacco in other media blood pressure bottom number low buy digoxin online now. Together 359 Media Use the national surveys cited above also assessed media use by children and adolescents. These young Americans are considered most vulnerable to the effects of media messages, and much of the research discussed here addresses the effects of media on their use of tobacco. Role of Entertainment Media with the existing body of knowledge surrounding the portrayal of tobacco use in movies, this chapter forms a base for future work on the impact of entertainment media on tobacco-related health issues. Historical Perspective: Movies Examination of the role of entertainment media in tobacco marketing is increasingly becoming an area of active research. Quantitative studies suggest that youth exposed to on-screen smoking are more likely themselves to initiate smoking. Pierce and Gilpin10 have identified four key periods in a historical analysis of tobacco marketing and smoking initiation among U. Campaigns explicitly targeted women, as exemplified by the Lucky Strike "Reach for a Lucky Instead of a Sweet" print media campaign during that period. However, the cigarette also was positioned as a symbol of independence and equality for women. At about the same time, Chesterfield rolled out a campaign aimed at changing social norms regarding smoking, with an emphasis on the social interaction between men and women. The campaign was launched by a 1926 billboard depicting a man who is smoking, seated next 360 Early Lucky Strike advertisement targeted at women to a woman who asks him to "blow some my way. Chesterfield advertisements regularly featured glamour photographs of a Chesterfield "girl of the month, " primarily fashion models and Hollywood starlets. Some endorsers were actresses, including Joan Bennett, Claudette Colbert, Joan Crawford, Betty Grable, Rita Hayworth, Marion Hutton, and Rosalind Russell. During the late 1940s, the advertisements continued to feature glamorous women but also included male stars. Star endorsements during this period included Charles Boyer, Perry Como, Bing Crosby, Arthur Godfrey, Bob Hope, Dorothy Lamour, Virginia Mayo, Ethel Merman, Gregory Peck, Basil Rathbone, Ann Sheridan, Jo Stafford, and James Stewart. From 1943 through 1946, advertisements for the Regent brand of cigarettes featured drawings of celebrities, including Fred Astaire, Diana Barrymore, Joan Blondell, Bing Crosby, Robert Cummings, Jinx Falkenberg, Arlene Francis, June Havoc, Celeste Holm, Guy Lombardo, Merle Oberon, and Jane Wyatt. The Role of the Media that era were beginning to perceive the potential power of celebrities and the media (including motion pictures) as ways to change social norms around smoking. After 1939, and through the mid-1960s, tobacco marketing no longer focused on any particular subgroup. Attending motion pictures was a national pastime by 1940, with Americans spending almost one-quarter of their total recreation dollars on movies Chesterfield cigarette advertisement featuring actress Joan Crawford Note: from Ladies Home Journal 1949 mutually beneficial relationship between the cigarette industry and the movie industry. It would be reasonable to assume that the stars were paid for their appearances in the advertisements as well as receiving nonmonetary benefits, such as increased exposure. Role of Entertainment Media Smoking: A Requirement of the Role One case report describes an actor being introduced to smoking on the set of his first movie. In a New York Times Op Ed column, a Kirk Douglas states he never smoked during his Broadway career in the early 1940s. But I had spoken only a few lines when the director, Lewis Milestone, stopped the action and said, "Kirk, you should be smoking a cigarette in this scene. Bette Davis plays a young Boston socialite who has been repressed and dominated by her mother. She smokes surreptitiously until she meets and falls in love with an older man (Paul Henreid) on a cruise. The sequence is captured at the close of the voyage, when Henreid lights two cigarettes and hands one to his lover just before a parting embrace. Given the popularity of this movie and these stars at the time, this sequence may have influenced the socialization of women to take up smoking, in part by teaching men a novel way to offer a cigarette to a woman. Although no direct evidence supports an advertising motive 362 for such scenes, they mirror the romantic themes included in cigarette advertising at the time, as illustrated by the Lucky Strike advertisements from the mid-1930s.