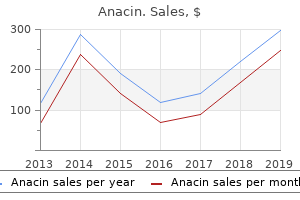
"Generic 525 mg anacin with amex, laser pain treatment reviews".
By: I. Shakyor, M.A., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, CUNY School of Medicine
Improved monomeric red drug treatment for shingles pain buy anacin now, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp neck pain treatment kerala order anacin cheap online. Because effective treatment of this disease depends on early and correct diagnosis arizona pain treatment center mcdowell anacin 525mg, you need to be able to detect the very low levels of this virus that are present in infected animals before the onset of disease symptoms. Briefly explain how you would proceed and why you have chosen a particular course of action. Why is it useful to simultaneously employ several different-color fluorescent proteins Most of these sequences have been expressed in mammalian as well as bacterial host cells, and currently more than 500 are undergoing clinical testing with human subjects for the treatment of various diseases. More than 250 of these "biotechnology drugs" have been approved for use in the United States or the European Union (Table 10. However, it will be several years before many of the other proteins are commercially available, because medical products must first be tested rigorously in animals and then undergo thorough human trials, which can last for several years, before being approved for general use. It has been estimated that in 2006 the annual global market for human recombinant protein drugs was about $60 billion. For example, in 2006, rituximab (Rituxan), a monoclonal antibody used to treat individuals with nonHodgkin lymphoma, generated nearly $4 billion in sales, while various forms of recombinant human insulin generated around $2. The development of preventive procedures and treatments for human diseases was the outstanding contribution of medicine and science to human well-being in the 20th century. The idea of using antibodies as therapeutic agents has come to fruition in the past several years, and specific antibodies are being tested to attack toxins, bacteria, viruses, and even cancer cells. In some cases, the target protein is isolated and a portion of the amino acid sequence is determined. Alternatively, antibodies are raised against the purified protein and used to screen a gene expression library. Pools of clones, rather than individual clones, were tested to speed up the identification process. Positive pools were divided into eight subgroups of 64 clones each and retested. Hepatitis C virus infection is one of the most common causes of liver disease, which affects nearly 200 million people worldwide. Many of these individuals eventually develop either cirrhosis of the liver or hepatocellular carcinoma. Therapeutic agents that maximize early antiviral response and maintain viral suppression throughout the course of therapy have the best chance of achieving lasting eradication of the virus from an infected individual. On the other hand, with the albumininterferon hybrid molecule, the drug (in this case, the fusion protein) in serum remains at a therapeutically effective level for a much longer time, so that it needs to be administered no more than once every 2 weeks. The initial clinical trials of the albumin-interferon hybrid molecule have all been positive. If these trials are successful, then the albumininterferon hybrid molecule may be available for general use some time in 2010. Insulin-like growth factor 1 is an essential component of the promotion of growth in children, and in adults, it controls metabolism. Human growth hormone was one of the first therapeutic proteins in the world to be approved for human use. Infants and children who lack sufficient endogenous levels of human growth hormone, patients with chronic renal insufficiency (defective kidneys), and individuals with Turner syndrome respond to treatment with growth hormone, which stimulates tissue and bone growth, increases protein synthesis and mineral retention, and decreases body fat storage. The first recombinant growth hormone was called somatrem (Protropin); it was produced and marketed by Genentech beginning in 1985. It had an amino acid sequence that was identical to that of human growth hormone, except that there was an extra methionine residue at the N-terminal end of the peptide chain (which was thought to prolong its half-life). Treatment of children with human growth hormone typically entails daily injections during the years when the child is growing. The cost of the treatment varies depending on the country and the size of the child but is generally approximately $10,000 to $30,000 per year. Scientists working at universities, research institutes, and drug and biotechnology companies are continually discovering and testing new molecules, as well as new uses for known compounds. However, it is impossible to know with any certainty which avenues of research will eventually bear fruit. Once a promising result has been obtained in the laboratory, and it has been shown to be reproducible, sufficient quantities of a highly purified version of the potential therapeutic compound must be produced so that it can be tested on small animals, such as mice. Based on the preclinical research data that are provided, about 85% of these applications are approved.
In an observational study of 33 patients with renal insufficiency undergoing liver transplantation pain research treatment impact factor cheap 525mg anacin fast delivery, 36% of patients who did not receive preemptive antifungal therapy vs joint & pain treatment center buy cheap anacin 525 mg online. A recently completed but unpublished study evaluating the effectiveness of fluconazole 400 mg/day or lower dose liposomal amphotericin (2 mg/kg/day) as preemptive therapy in high-risk liver transplant recipients should more accurately address the appropriateness of this approach in a welldefined population shoulder pain treatment options generic 525 mg anacin otc. Some authors have advocated preemptive therapy in discreet clinical situations that include pulmonary colonization with Aspergillus spp. In a prospective, nonrandomized and openlabel study of preemptive antifungal therapy, 26 lung transplant recipients with fungal colonization of the tracheobronchial tree were given either fluconazole or itraconazole until the surgical anastomoses appeared normal and cultures were consistently negative. Only 2(8%) of 26 patients in this study developed Aspergillus tracheobronchitis (Hamacker et al, 1999). The largest study to date compared fluconazole 400 mg daily to placebo given for the first 70 days posttransplant among 212 liver transplant recipients in a randomized, double-blind study. In a small, randomized, double-blind study of 86 liver transplant patients, 0% vs. Recent studies among lung transplant recipients have examined the use of inhaled amphotericin B preparations for primary prophylaxis of invasive fungal pneumonia and bronchitis. Hospitalizations for fungal infections after renal transplantation in the United States. Agarwal S K, Tiwari S C, Dash S C, Mehta S N, Saxena S, Banerjee U, Kumar R, Bhunyan U N. Argenziano M, Catanese K A, Moazami N, Gardocki M T, Weinberg A D, Clavenna M W, Rose E A, Scully B E, Levin H R, Oz M C. The influence of infection on survival and successful transplantation in patients with left ventricular assist devices. Bacal F, Andrade A C, Migueletto B C, Bocchi E A, Stolf N A, Fiorelli A I, Strabelli T M, Benvenuti L A, Brandao C M, Bellotti G, Ramires J A. True mycotic arteritis by Candida albicans in 2 kidney transplant recipients from the same donor. Fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients Benedetti E, Gruessner A C, Troppmann C, Papalois B E, Sutherland D E, Dunn D L, Gruessner R W. Intra-abdominal fungal infections after pancreatic transplantation: incidence, treatment, and outcome. Bernabeu-Wittel M, Naranjo M, Cisneros J M, Canas E, Gentil M A, Algarra G, Pereira P, Gonzalez-Roncero F J, de Alarcon A, Pachon J. Infections in renal transplant recipients receiving mycophenolate versus azathioprine-based immunosuppression. Cutaneous hyalohyphomycosis caused by Paecilomyces lilacinus in a renal transplant patient. A case of disseminated histoplasmosis likely due to infection from a liver allograft. Caecal perforation in a renal transplant patient with disseminated histoplasmosis. Incidence of significance of Aspergillus cultures following liver and kidney transplantation. Cerebral aspergillosis: long term efficacy and safety of liposomal amphotericin B in kidney transplant. Chkhotua A, Yussim A, Tovar A, Weinberger M, Sobolev V, BarNathan N, Shaharabani E, Shapira Z, Mor E. Candida polyarthritis in a renal transplant patient: case report of a patient successfully treated with amphotericin B. Destructive allograft fungal arteritis following simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Clinical significance to Scedosporium apiospermum in patients with cystic fibrosis. Paecillomyces lilacinus infection in a heart transplant 483 recipient and successful treatment with terbinafine. Collins L A, Samore M H, Roberts M S, Luzzati R, Jenkins R L, Lewis W D, Karchmer A W.
Concomitant therapy with antiepileptic drugs phantom limb pain treatment guidelines buy anacin 525 mg with mastercard, erectile dysfunction drugs pain treatment while on suboxone order anacin online pills, colchicine sacroiliac joint pain treatment exercises purchase anacin 525 mg otc, and azole antifungals must be undertaken with caution. Dosing of the proton pump inhibitor should be separated by 12 hrs from the atazanavir/ritonavir. If other acid suppressants are used with atazanavir, the doses must be separated by as much time as possible (up to 12 hrs apart). The dose of clarithromycin should be decreased by 50%, or alternative therapy considered. Its dosing is dependent on treatment experience and number of resistance mutations present. Fosamprenavir has largely replaced amprenavir because of its improved dosing convenience. Infectious Diseases 733 (3) Precautions and monitoring effects (a) Fosamprenavir may be dosed once daily in treatment-naive patients. Combination therapy with atazanavir is not recommended owing to the potential for additive effects. This product is available as a coformulation of lopinavir with a "booster" dose of ritonavir, which inhibits lopinavir metabolism and results in higher serum concentrations. Nelfinavir decreases methadone concentrations, necessitating increased monitoring and dose adjustment if indicated. A tablet formulation is also available that does not require refrigeration and should be taken with food. Many drug interactions occur with ritonavir because it is such a potent inhibitor of so many cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. Use of saquinavir without booster doses of ritonavir is not recommended because of the poor bioavailability of saquinavir. Liver function tests should be monitored closely, especially in patients with underlying liver disease. Enfuvirtide (T-20; Fuzeon) is the first and only member of this class of antiretrovirals. Enfuvirtide is primarily used in highly treatment-experienced patients with extensive viral resistance. It is not recommended for use as initial therapy in treatment-naive patients, as it has not been studied in this population. Precautions and monitoring effects (1) Enfuvirtide is injected subcutaneously twice daily. Local injection site reactions occur in almost all patients, including pain, redness, pruritus, and nodules. Maraviroc (Selzentry) is the first and only member of this class of antiretroviral therapy. Precautions and monitoring effects (1) Hepatotoxicity was observed during clinical trials with maraviroc (black box warning). Raltegravir (Isentress) is the first and only member of this class of antiretroviral therapy. Precautions and monitoring effects (1) Because elevations in creatine kinase, along with myopathy and rhabdomyolysis, may occur with raltegravir, use with caution in patients who are receiving concomitant medications that may cause these adverse effects. Because rifampin decreases the serum concentration of raltegravir, the dose of raltegravir should be increased to 800 mg twice daily when used concomitantly. Monotherapy with these agents is unacceptable, as the development of resistance with subsequent virologic failure occurs rapidly. It is added to interferon alfa and ribavirin following 4 weeks of t reatment with those two agents. Patients should be counseled on how to avoid missing or delaying doses in order to optimize the effectiveness of this agent. Avoid concomitant use with alfuzosin, rifampin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, ergot alkaloids, St.
Macrophages are phagocytic cells that rid the body of dead cells breast pain treatment vitamin e buy anacin 525mg without a prescription, cellular debris back pain treatment london cheap anacin, and serve as sentinel cells for the early detection of infection and tissue damage pain treatment plan buy genuine anacin on-line. They also produce cytokines that activate inflammation, recruit leukocytes such as neutrophils and additional macrophages to the site of the infection, and assist in activating the adaptive immune response by serving as antigen-presenting cells for T cells. Dendritic cells are branched or dendritic-shaped cells that are very effective for initiating T-cell responses. Dendritic cells are resident within the tissues of the body, where they are phagocytic. They then enter the lymphatics to travel to the local secondary lymph tissue, where they express additional adhesins for interaction with T cells and present the antigens from the peripheral tissues. All B and T lymphocytes are antigen specific via antigen receptors on the cell surface. Lymphocyte antigen receptors structurally consist of globular protein motifs know as immunoglobulin (Ig) domains. Ig domains are characteristic of many cell surface and secreted proteins of the immune system. In this chapter, the terms B cell and T cell are used instead of B lymphocyte and T lymphocyte. The antibody is roughly "Y" shaped with the transmembrane region positioned in the stem of the "Y" and the antigen-binding region at the ends of the arms. Binding of the specific antigen stimulates the B cell for proliferation to form new B cells (clonal expansion) and differentiation into plasma cells, which secrete free-soluble antibody (Figure 57-1). During development in the bone marrow, progenitor cells give rise to a large number of B cells, each with different surface-expressed antibodies with different antigen specificity. Antibodies are able to bind antigens directly and do not require any processing of the antigen in order to bind to the corresponding epitope. During an infection, only those B cells with antibodies able to bind to the antigens are activated. Proliferation of pathogen-activated B cells and differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells will give rise to antibodies able to act in the adaptive immune response to the infection. Immunology 1105 have different antigen specificity, but each T cell has only one specificity. Different T cells have different antigen specificity, but each T cell has only one specificity. B (2) Naive T cells are those that are mature but have not yet encounter the specific antigen for activation. The effector activity of the T cell depends on the type of T cell and the environment of the activation. Acute-phase proteins include C-reactive protein, mannose-binding lectin, and fibrinogen. Primary immune organs (thymus and bone marrow) are the sites of lymphocyte development and maturation. The creation of the antigen-specific receptors of the lymphocytes occurs during development in the primary organs before the lymphocyte encounters antigen. B-cell development occurs in the bone marrow; T-cell development begins in the bone marrow and finishes in the thymus. Secondary immune tissues are the sites throughout the body where antigen-specific lymphocytes contact antigens. Antigens enter the different types of secondary lymph tissues via different mechanisms. Both B and T cells circulate throughout the body, passing through the secondary lymphoid tissue. Each secondary lymph tissue has T- and B-cell zones for activation and differentiation of lymphocytes. Upon immune stimulation, activation of appropriate B and T cells will lead to the formation of germinal centers, which are areas of intense B-cell proliferation and differentiation. Fluid (lymph) from extravascular spaces is collected in the lymphatic vessels and returned to the circulation via the left subclavian vein. The naive lymphocytes enter the lymph node via the blood vessels and migrate to their respective B- and T-cell zones. Free antigens from the tissue, dendritic cells (with processed antigen), and immune complexes enter the lymph node in the lymph.