"Purchase cyclophosphamide once a day, medicine x topol 2015".
By: W. Bufford, MD
Vice Chair, College of Osteopathic Medicine of the Pacific, Northwest
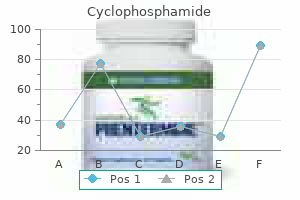
The authors suggested that the observed effects were probably due to symptoms of 50 mg cyclophosphamide overnight delivery decreased activity of tyrosine hydroxylase and increased levels of monoamine oxidase treatment walking pneumonia purchase cyclophosphamide 50mg amex. The authors performed neurochemical analyses of hypothalamus and corpus striatum as before and observed that serotonin was increased in the hypothalamus at the highest dose symptoms just before giving birth order cyclophosphamide 50 mg fast delivery, but was not elevated significantly in the striatum. Acetylcholinesterase levels were significantly decreased in the striatum at the highest dose, but were unchanged in the hypothalamus. The authors believed that the decrease in acetylcholinesterase to be of minor functional significance given that other mechanisms can also regulate acetylcholine metabolism. A study by Kontur and Fechter (1988) reported no difference in levels of monoamines and related metabolites in neonatal rats at 22 mg manganese/kg/day as manganese chloride (1421 days), although Dorman et al. There was a significant decrease in body weight gain in pups at the highest manganese exposure dose. However, in adult rats, the amplitude of the acoustic startle reflex was significantly decreased compared to the control at the lowest dose tested. The only behavioral end point affected during the neonatal period was a significant (p<0. The results indicate that neonatal exposure of rats to excess manganese caused subtle behavioral effects (altered balance in the neonatal period and diminished locomotor response to cocaine in adulthood) and neurochemical effects in adulthood (decreased dopamine binding sites in the striatum). The two highest dose groups of rats took approximately twice as long (2 seconds) as control and 0. The control group required approximately 40 seconds; the high-dose group required 75 seconds (an 88% increase in the high-dose group over the control). In the passive avoidance task, there was a positive linear trend, with the highest dose group showing a 3-fold increase in the number of footshocks received over the control. A negative linear relationship was also observed in striatal dopamine concentrations, with the high-dose group having approximately half the dopamine concentration of the control. No dose-related trends over time points were observed in manganese content of tissues. Again, Sprague-Dawley rat pups received dietary supplementation in the form of 0, 0. Male and female pups were sacrificed during infancy and at weaning (1824 per treatment group) for tissue analyses of trace elements. No statistically significant results for any individual treatment group for any behavioral task or striatal dopamine levels. A statistically significant positive trend was observed for passive avoidance (approximately 50% more footshocks in highest dose group, compared with control). Dose groups were balanced across sex within each of 26 litters, each culled to 10 pups with an approximate 2:1 male to female ratio. All treated males had increased stereotypical behavior in the radial arm maze (p<0. Additionally, there were significant decreases in dopamine D1 and D2 receptors and dopamine transporter in multiple brain regions from males from the 50 mg/kg/day group. In a follow-up study, Kern and Smith (2011) evaluated the effects of preweaning manganese exposure on the adult dopaminergic system, behavior, and astrocytic activation. Sprague-Dawley rat pups were exposed to 0, 25, or 50 mg manganese/kg/day using the experimental design described above. At 50 mg/kg/day, additional regions in the adult brain had significantly increased atrocytic activation (prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens). In the open field, there were no measureable differences in activity in adults (compared to increased activity in weanlings reported in the previous study). However, a residual effect could be observed under the influence of D-amphetamine. In order to determine if developing animals are more susceptible to the neurochemical and neurobehavioral effects of manganese exposure, Moreno et al. Littermates from timed-pregnant C57Bl/6 mice were paired in control and manganese-exposed groups, receiving 0, 4. Open field activity was measured every other day during early exposure (1118 animal/group), and every other week thereafter (810 animals/group). Brain levels of manganese, iron, and copper were also measured in three animals per group. In all treated animals, brain regions with the highest levels of manganese were striatum, substantia nigra, and cortex.
Your arrangements might be right lung-group A-lymph node treatment pneumonia purchase cyclophosphamide online now, in one zap followed by right lunggroup L-lymph node in a second zap treatment leukemia generic 50mg cyclophosphamide amex. Example 4: Lymph nodes associated with various portions of the intestinal tract can be found by placing the access routes between the lymph node and intestinal slide treatment bronchitis discount cyclophosphamide 50mg on-line. Since these portions are quite long, this still leaves a measure of precision to be desired. Example 5: Lymph nodes in the groin area are often painful or enlarged for various reasons. These may be reachable beginning with a sacral spinal cord slide contacting the sacrum (bone), which, in turn, is contacted by an access route, and finally by a lymph node slide. Conclusion: the rule for discovering the electronic location of an organ is to find its true physical connection to another organ. This is best exemplified by noting that you can zap two adjacent vertebrae by touching them together on the plate, but you cannot zap any other two in a single zap. Materials: Two identical quarters or dimes (for small regions), a paper dowel standoff to hold the coin tightly against skin, several slides of organ sought. To make a paper dowel standoff fold a double paper towel in half lengthwise, twice. Hold its mate over the lymph node to be electronically "found" somewhere below the skin areas, using the paper dowel. If searching for two minutes does not yield a Positive result, try yet another lymph node slide. The right and left organs of a pair do not resonate, whereas two rights or two lefts do. Purpose: To find right and left organ slides or specimens; to identify your slides. For example kidney, lung, adrenal, leg bones, arm bones, eyes, thyroid, thymus, liver (this also has a middle region). Place a coin (quarter or dime preferred) on the skin over the spot you believe is on top of the organ, for example kidney. Press the coin on the skin with a paper dowel (with at least an inch of standoff distance), while testing for resonance. If there is no resonance, move the skin coin to new locations in the same vicinity in an effort to find the organ (kidney). If you find a location that resonates, you have found this organ on the current path traced out by the Syncrometer. In other words, the time is going into an even minute (This is my definition, not an official one). But when they occur along scars from previous surgery, they may have no identification. Even though the original cancer stemmed from the lung or stomach the new tumors may not. Many other kinds of tumors are also without identification; yet need to be "found". Materials: Two cat skeletons, one assembled, and one taken apart (see Supplies Used For Testing page 161), anatomy set of slides, toxin kit. Methods: If you can actually feel the tumor or lump you may get an idea where it is in relation to the nearest organs. Attach a tricalcium phosphate specimen (representing tumor) to the duo; now you have the neighboring organ, touching the arteries of group A, which is further touched by tricalciumphosphate (a trio). If they are Negative, repeat the test using the lymphatic group (L) in the middle of the series instead of the arterial group. Note: From a practical standpoint, you can of course zap these neighboring organs anyway, since this is returning more and more immune power to you. But the principle that is made clear in this experiment is that you can mimic the actual connections of tissues with electrical connections and find that you can locate otherwise unidentifiable regions for study or for zapping.
The most common hookworm of the Americas is Necator americanus (new world hookworm) treatment goals and objectives purchase online cyclophosphamide. Because many specimens are poorly oriented so that the plates are not clearly seen symptoms valley fever cheap generic cyclophosphamide uk, you do not have to medications causing thrombocytopenia order cyclophosphamide on line distinguish genera of hookworms from one another on sight. However, as stated above, you should know the differences between the two genera if I state whether a particular specimen has teeth or cutting plates. The eggs of hookworms cannot easily be distinguished from one another by a novice. They are fairly thin walled and in the morula stage (generally the 4, 8, 16, or 32 cell stage). The walls of many hookworm eggs appear to have been dissolved during specimen processing (at least with our slides) and, thus, may be difficult to discern initially. The easiest way to find these eggs is to scan your slide using a 10x objective lens (100x total magnification) and identify the morulas. Then, switch the objective to 40x (400x total magnification) to better see the egg wall. Eggs are easily distinguished because they are subspherical and possess a thick, mammillated wall. You should be able to distinguish 3 types of eggs: 1) a fertilized egg with the mammillated wall; 2) a fertilized egg where the rough outer wall has been strippped away; and 3) an unfertilized egg which is generally longer and narrower than fertilized ones, the internal details appear as disorganized globules, and and the inner chitinous and lipid wall layers are not formed. These larvae are microscopic L1 stages that can be seen coiled within individual skeletal muscle cells. The technically correct name for this species is Calodium hepaticum, although few textbooks have yet made the conversion. Adults are found in the liver, although it is unlikely that you will see a cross-section through one. The female produces numerous eggs that are retained and encapsulated within the liver parenchyma. Eggs are similar to Trichuris in that they have bipolar plugs in either end, however, they tend to be more squared off at the ends than Trichuris. Once the eggs are liberated into the environment, either by passing through the gut of a carnivore or following host decomposition, eggs embryonate and become infective. Related species known to infect humans and for which eggs may be found in human feces include Aonchotheca philippinensis (Capillaria philippinensis), an intestinal parasite normally using a bird/fish life-cycle, and Eucoleus aerophilus (Capillaria aerophilus), a respiratory tract parasite of carnivores. Adults live in subcutaneous nodules and produce microfilariae that wander throughout the skin. These larvae are unsheathed (without an embryonic membrane) and have a tapered, flexed tail. Adults of the first two species live in lymphatics and produce microfilariae that circulate in the bloodstream. Adults of Loa loa wander throughout the dermis and produce microfilariae that also enter the bloodstream. Larvae of all species have an embryonic sheath, tapered tail, and are difficult to tell apart without a good stain. Based on the above information and that in your text, you should know the following key characters for differentiating Onchocerca volvulus, Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and Loa loa: 1) Whether the microfiliariae are sheathed or non-sheathed. Demonstration: Know how to distinguish female Ascaris lumbricoides (large; straight tail) from males (smaller; hooked tail). Demonstration: Dioctophyma renale are the largest of the worms you will be examining. Adults occur in the kidneys, and eggs with bipolar plugs somewhat like Capillaria hepatica pass out with the urine. Females are much larger than males, and do not have the copulatory bursa of the male. You will only need to know the five items listed earlier for Brugia malayi, Loa loa, Onchocerca volvulus, and Wuchereria bancrofti.