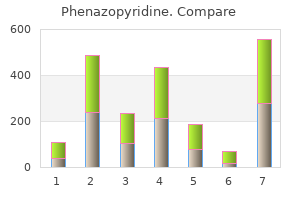
"Discount phenazopyridine 200mg fast delivery, gastritis diet therapy".
By: S. Raid, MD
Co-Director, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, Temple University
The fused basement membrane separates the endothelium of glomerular capillary and the epithelium of visceral layer of Bowman capsule gastritis diet food recipes buy discount phenazopyridine 200 mg online. Visceral layer of Bowman capsule this layer is formed by a single layer of flattened epi thelial cells resting on a basement membrane gastritis diet for dogs buy phenazopyridine 200mg with visa. Each cell is connected with the basement membrane by cytoplasmic extensions called pedicles or feet gastritis test order discount phenazopyridine on line. When blood passes through glomerular capillaries, the plasma is filtered into the Bowman capsule. Ultrafiltration Glomerular filtration is called ultrafiltration because even the minute particles are filtered. The protein molecules are larger than the slit pores present in the endothelium of capillaries. Thus, the glomerular filtrate contains all the substances present in plasma except the plasma proteins. This technique involves insertion of a micropipette into the Bowman capsule and aspiration of filtrate. Glomerular capillary membrane Glomerular capillary membrane is formed by single layer of endothelial cells, which are attached to the basement membrane. The capillary membrane has many pores called fenestrae or filtration pores with a diameter of 0. Chapter 52 t Urine Formation 317 between renal plasma flow and glomerular filtration rate. Starling Hypothesis and Starling Forces Determination of net filtration pressure is based on Starling hypothesis. Starling hypothesis states that the net filtration through capillary membrane is proportional to hydrostatic pressure difference across the membrane minus oncotic pressure difference. Hydrostatic pressure within the glomerular capillaries is the glomerular capillary pressure. All the pressures involved in determination of filtration are called Starling forces. Glomerular Capillary Pressure Glomerular capillary pressure is the pressure exerted by the blood in glomerular capillaries. Colloidal Osmotic Pressure It is the pressure exerted by plasma proteins in the glomeruli. The plasma proteins are not filtered through the glomerular capillaries and remain in the glomerular capillaries. Hydrostatic Pressure in Bowman Capsule It is the pressure exerted by the filtrate in Bowman capsule. Net Filtration Pressure Net filtration pressure is the balance between pressure favoring filtration and pressures opposing filtration. Renal Blood Flow It is the most important factor that is necessary for glomerular filtration. Macula densa of juxtaglomerular apparatus in the terminal portion of thick ascending limb is sensitive to the sodium chloride in the tubular fluid. When the glomerular filtrate passes through the terminal portion of thick ascending segment, macula densa acts like a sensor. When the concentration of sodium chloride increases in the filtrate essential filtration pressure. Glomerular Capillary Pressure Glomerular filtration rate is directly proportional to glomerular capillary pressure. Capillary pressure, in turn depends upon the renal blood flow and arterial blood pressure. Colloidal Osmotic Pressure Glomerular filtration rate is inversely proportional to colloidal osmotic pressure, which is exerted by plasma proteins in the glomerular capillary blood. Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman capsule increases in conditions like obstruction of urethra and edema of kidney beneath renal capsule. Later when all the substances are filtered from this blood, further filtration does not occur. It is because, the efferent arteriolar constriction prevents outflow of blood from glomerulus and no fresh blood enters the glomerulus for filtration. There are several other factors, which increase or decrease the sensitivity of tubuloglomerular feedback. The Chapter 52 t Urine Formation 319 accordingly, because the autoregulatory mechanism fails beyond this range.
These metabolites dilate the blood vessels and bring the blood flow back to gastritis diet of the stars 200 mg phenazopyridine otc normal gastritis symptoms bad breath order phenazopyridine 200 mg overnight delivery. Conversely gastritis symptoms bupa order on line phenazopyridine, when blood flow increases, the vasodilator metabolites are washed out of the tissues quickly. However, autoregulation is more effective in some of the vital organs like kidney (Chapter 51), heart (Chapter 108) and brain (Chapter 109). To determine the mean pressure, diastolic pressure is considered than the systolic pressure. Formula to calculate mean arterial blood pressure: Mean arterial blood pressure = Diastolic pressure + 1/3 of pulse pressure = 80 + 40 3 = 93. Systolic pressure is subjected for variations easily and quickly and its variation occurs in a wider range. Diastolic pressure is not subjected for easy and quick variations and its variation occurs in a narrow range. Systolic pressure in different age Newborn After 1 month After 6 month After 1 year At puberty At 50 years At 70 years At 80 years Newborn After 1 month After 6 month After 1 year At puberty At 50 years At 70 years At 80 years 2. Sex In females, up to the period of menopause, arterial pressure is 5 mm Hg, less than in males of same age. After menopause, the pressure in females becomes equal to that in males of same age. After Meals Arterial blood pressure is increased for few hours after meals due to increase in cardiac output. During Sleep Usually, the pressure is reduced up to 15 to 20 mm Hg during deep sleep. Emotional Conditions During excitement or anxiety, the blood pressure is increased due to release of adrenaline. After Exercise After moderate exercise, systolic pressure increases by 20 to 30 mm Hg above the basal level due to increase in rate and force of contraction and stroke volume. It is because, the diastolic pressure depends upon peripheral resistance, which is not altered by moderate exercise. After severe muscular exercise, systolic pressure rises by 40 to 50 mm Hg above the basal level. But, the diastolic pressure reduces because the peripheral resistance decreases in severe muscular exercise. Blood volume Venous return Elasticity of blood vessels Velocity of blood flow Diameter of blood vessels Viscosity of blood. Whenever the cardiac output increases, the systolic pressure is increased and when cardiac output is less, the systolic pressure is reduced. In conditions like myocardial infarction, the cardiac output decreases, resulting in fall in systolic pressure. Heart Rate Moderate changes in heart rate do not affect arterial blood pressure much. However, marked alteration in the heart rate affects the blood pressure by altering cardiac output (Chapter 98). Peripheral Resistance Peripheral resistance is the important factor, which maintains diastolic pressure. Peripheral resistance is the resistance offered to the blood flow at the periphery. When peripheral resistance increases, diastolic pressure is increased and when peripheral resistance decreases, the diastolic pressure is decreased. These factors are called local factors, mechanical factors or determinants of blood pressure (Table 103. Peripheral resistance Arterial blood pressure is directly proportional to Arterial blood pressure is inversely proportional to Chapter 103 t Arterial Blood Pressure 605 4. Blood volume maintains the blood pressure through the venous return and cardiac output. If the blood volume increases, there is an increase in venous return and cardiac output, resulting in elevation of blood pressure.
In this example gastritis liver buy 200 mg phenazopyridine with visa, the disease frequency gastritis symptoms and remedies buy cheap phenazopyridine on-line, q2 mild gastritis diet buy generic phenazopyridine on-line, is 1/100, and the allele frequency, q, is 1/10, or 0. Using the assumption that the normal allele frequency, p, is about 1 is not necessarily valid. With the application of the Hardy-Weinberg principle to this autosomal recessive disease, if 1/100 individuals are affected in a population, then q2 = 1/100 and q = 1/10, or 0. These alterations may involve the presence of extra chromosomes or the loss of chromosomes. Chromosome abnormalities are seen in approximately 1 in 150 livd births and are the leading known cause of mental retardation. Chromosomes are ordered according to size, with the sex chromosomes (X and Y) placed in the lower right portion of the karyotype. G-banding reveals a pattern of light and dark (G-bands) regions that allow chromosomes to be accurately identified in a karyotype. Cytoge~etics Chromosome abnormalities in some cases can be identified visually by looking at the banding pattern, but this technique reveals differences (for instance, larger deletions) only to a resolution of about 4 Mb. Submetacentric chromosomes have the centromere displaced toward one end (for example, chromosome 4). Only the acrocentric chromosomes are involved in Robertsonian translocations, which will be discussed in this chapter. Gametes (sperm and egg cells) are euploid cells that have 23 chromosomes (one member of each pair); they are said to be haploid. Most somatic cells are diploid, containing both members of each pair, or 46 chromosomes. Two types of euploid cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes are seen in humans: triploidy and tetraploidy. Triploidy refers to cells that contain three copies of each chromosome (69 total)! Triploidy, which usually occurs as a result of the fertilization of an ovum by two sperm cells, is common at conception, but the vast majority of these conceptions are lost prenatally. These babies have multiple defects of the heart and central nervous system, and they do not survive. Tetraploidy refers to cells that contain four copies of each chromosome (92 total): this lethal condition is much rarer than triploidy among live births: Only a few cases have been described. Aneuploidy Aneuploidy, a deviation from the euploid number, represents the gain (+) or loss (-) of a specific chromosome. If more than one X chromosome is present, all but one will become a Barr body in each cell. The two important sex chromosome aneuploidies are Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome. Edema of wrists and ankles in newborn Cystic hygroma in utero resulting in excess nuchal skin and "webbed" neck Primary amenorrhea Coarctation of the aorta or other congenital heart defect in some cases Infertility Gonadal dysgenesis. In this case, the sister chromatids of a chromosome (for example, chromosome 21) fail to segregate (disjoiri). Some important points to remember: Nondisjunction is the usual cause of aneuploidies including Down, Edward, and Patau syndromes as well as Turner and Kleinfelter syndromes. I the risk of bearing a child with Down syndrome is less than 1/1,006 for women younger than 30. The risk increases to about 1/400 at age 35, 1/100 at age 40, and 3-4% or more after age 45. The increased risk of trisomy with advanced maternal age motivates more than half of pregnant women in North America to undergo prenatal diagnosis (most commonly, amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, discussed in Chapter 6). Down syndrome can also be screened by assaying maternal serum levels of a-fetoprotein, chorionic gonadotropin, and unconjugated estriol. This so-called triple screen can detect approximately 70% of fetuses with Down syndrome. In Anaphase 2, sister chromatids migrate to opposite poles and each daughter cell gets one chromatid!
Buy phenazopyridine online. What is best to eat after a stomach bug ? | Best and Top Health FAQs.
The initial reaction of -alanine catabolism is transamination to gastritis sintomas buy phenazopyridine with mastercard malonate semialdehyde gastritis symptoms tagalog discount 200 mg phenazopyridine with mastercard. Disorders of -alanine and -aminoisobutyrate metabolism arise from defects in enzymes of the pyrimidine catabolic pathway gastritis diet 40 purchase phenazopyridine 200 mg without a prescription. Biosynthesis of carnosine is catalyzed by carnosine synthetase in a twostage reaction that involves initial formation of an enzymebound acyl-adenylate of -alanine and subsequent transfer of the -alanyl moiety to l-histidine. Conversion of glycine and the guanidine group of arginine to creatine and creatine phosphate. Homocarnosinosis, a rare genetic disorder, is associated with progressive spastic paraplegia and mental retardation. Via ornithine, arginine provides the skeleton of the polyamines putrescine, spermine and spermidine. Cysteine provides the thioethanolamine portion of coenzyme A, and following its conversion to taurine, part of the bile acid taurocholic acid. Glycine participates in the biosynthesis of heme, purines, creatine, and N-methylglycine (sarcosine). Many drugs and drug metabolites are excreted as glycine conjugates, which increases water solubility for urinary excretion. Histidine compounds present in the human body include ergothioneine, carnosine, and dietary anserine. S-Adenosylmethionine, the principal source of methyl groups in metabolism, contributes its carbon skeleton to the biosynthesis of the polyamines spermine and spermidine. In addition to its roles in phospholipid and sphingosine biosynthesis, serine provides carbons 2 and 8 of purines and the methyl group of thymine. Kidney and liver tissue, and also fecal bacteria, convert tryptophan to tryptamine and thence to indole 3-acetate, the principal tryptophan catabolites in urine are indole 3-acetate and 5-hydroxyindoleacetate. Tyrosine forms norepinephrine and epinephrine, and following iodination the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine and thyroxine. The enzyme-catalyzed interconversion of the phospho- and dephospho-forms of peptide bound serine, threonine and tyrosine plays key roles in metabolic regulation, including signal transduction. Glycine, arginine, and S-adenosylmethionine all participate in the biosynthesis of creatine, which as creatine phosphate serves as a major energy reserve in muscle and brain tissue. Excretion in the urine of its catabolite creatine is proportionate to muscle mass. Disorders of -alanine and -aminoisobutyrate metabolism arise from defects in enzymes of pyrimidine catabolism. Wu F et al: Inhibitory and structural studies of novel coenzymesubstrate analogs of human histidine decarboxylase. These topics are closely related, because heme is synthesized from porphyrins and iron, and the products of degradation of heme are the bile pigments and iron. Knowledge of the biochemistry of the porphyrins and of heme is basic to understanding the varied functions of hemoproteins (see below) in the body. As a simple means of showing these substitutions, Fischer proposed a shorthand formula in which the methyne bridges are omitted the functions of the above proteins are described in various chapters of this text. The two starting materials are succinylCoA, derived from the citric acid cycle in mitochondria, and the amino acid glycine. A porphyrin with a completely symmetric arrangement of the substituents is classified as a type I porphyrin. However, the porphyrinogens are readily auto-oxidized to their respective colored porphyrins. The mitochondrial enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase catalyzes the decarboxylation and oxidation of two propionic side chains to form proto- porphyrinogen.
The reactions are catalyzed by cysteine dioxygenase gastritis kidney pain order 200 mg phenazopyridine overnight delivery, cysteine sulfinate decarboxylase gastritis symptoms treatment diet phenazopyridine 200mg otc, and hypotaurine decarboxylase gastritis ibs diet generic phenazopyridine 200mg on-line, respectively. These polyamines function in cell proliferation and growth, are growth factors for cultured mammalian cells, and stabilize intact cells, subcellular organelles, and membranes. Urinary metabolites of serotonin in patients with carcinoid include N-acetylserotonin glucuronide and the glycine conjugate of 5-hydroxyindoleacetate. Serotonin and 5-meth- oxytryptamine are metabolized to the corresponding acids by monoamine oxidase. N-Acetylation of serotonin followed by its O-methylation in the pineal body forms melatonin. While dopa is also an intermediate in the formation of melanin, different enzymes hydroxylate tyrosine in melanocytes. Since the 24-h urinary excretion of creatinine is proportionate to muscle mass, it provides a measure of whether a complete 24-h urine specimen has been collected. Traces of -alanine also result from the hydrolysis of -alanyl dipeptides by the enzyme carnosinase. The oxidation of protoporphyrinogen to protoporphyrin is catalyzed by another mitochondrial enzyme, protoporphyrinogen oxidase. In mammalian liver, the conversion of coproporphyrinogen to protoporphyrin requires molecular oxygen. However, approximately 85% of heme synthesis occurs in erythroid precursor cells in the bone marrow and the majority of the remainder in hepatocytes. Most of these drugs are metabolized by a system in the liver that utilizes a specific hemoprotein, cytochrome P450 (see Chapter 53). The importance of some of these regulatory mechanisms is further discussed below when the porphyrias are described. This is a distinguishing feature of the porphyrin ring and is characteristic of all porphyrins regardless of the side chains present. An interesting application of the photodynamic properties of porphyrins is their possible use in the treatment of certain types of cancer, a procedure called cancer phototherapy. Thus, hematoporphyrin or other related compounds are administered to a patient with an appropriate tumor. They are not prevalent, but it is important to consider them in certain circumstances (eg, in the differential diagnosis of abdominal pain and of a variety of neuropsychiatric findings); otherwise, patients will be subjected to inappropriate treatments. Also, the photosensitivity (favoring nocturnal activities) and severe disfigurement exhibited by some victims of congenital erythropoietic porphyria have led to the suggestion that these individuals may have been the prototypes of so-called werewolves. Spectrophotometry Is Used to Test for Porphyrins & Their Precursors Coproporphyrins and uroporphyrins are of clinical interest because they are excreted in increased amounts in the porphyrias. These compounds, when present in urine or feces, can be separated from each other by extraction with appropriate solvent mixtures.