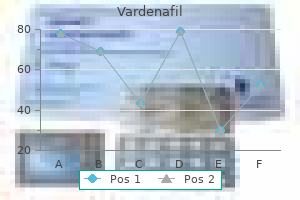
"Order vardenafil canada, erectile dysfunction at age 19".
By: I. Charles, M.A., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Homer G. Phillips College of Osteopathic Medicine
This often leads to erectile dysfunction medication cialis buy discount vardenafil on-line extreme parental frustration and anger erectile dysfunction treatment dallas generic vardenafil 10mg with amex, and the child may be inadequately nourished and developmentally and emotionally thwarted erectile dysfunction doctors in kansas city discount vardenafil 20mg overnight delivery. When the pediatrician is attempting to sort out the factors contributing to food refusal, it is essential first to obtain a complete history, including a social history. Medications such as phenobarbital elixir and dicyclomine have been found to be somewhat helpful, but their use is to be discouraged because of the risk of adverse reactions and overdosage. Children have feeding problems for various reasons including oral motor dysfunction, cardiopulmonary disorders leading to fatigue, gastrointestinal disturbances causing pain, social or emotional issues, and problems with regulation. Second, a complete physical examination should be performed, with emphasis on oral-motor behavior and other clues suggesting neurologic, anatomic, or physiologic abnormalities that could make feeding difficult. This is particularly important if there is concern about depression or a history of developmental delays. If evidence of oral-motor difficulty is suspected, evaluation by an occupational therapist is warranted. Finally, the physician needs to help the parents understand that infants and children may have different styles of eating and different food preferences and may refuse foods they do not like. Chatoor I et al: Failure to thrive and cognitive development in toddlers with infantile anorexia. When the chief complaint is failure to gain weight, a different approach is required. The differential diagnosis should include not only food refusal but also medical disorders and maltreatment. Excessive weight loss may be due to vomiting or diarrhea, to malabsorption, or to a combination of these factors. Laboratory studies may include a complete blood count; erythrocyte sedimentation rate; urinalysis and urine culture; blood urea nitrogen; serum electrolytes and creatinine; and stool examination for fat, occult blood, and ova and parasites. Occasionally an assessment of swallowing function or evaluation for the presence of gastroesophageal reflux may be indicated. Because of the complexity of the problem, a team approach to the diagnosis and treatment of failure to thrive, or poor weight gain, may be most appropriate. Occupational and physical therapists, developmentalists, and psychologists may be required. The goals of treatment of the child with poor weight gain are to establish a normal pattern of weight gain and to establish better family functioning. Adolescents-difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, or early morning awakening, or nonrestorative sleep, or a combination of these problems. Sleep is a complex physiologic process influenced by intrinsic biologic properties, temperament, cultural norms and expectations, and environmental conditions. Between 20% and 30% of children experience sleep disturbances at some point in the first 4 years of life. Dyssomnias refer to problems with initiating and maintaining sleep or to excessive sleepiness. Parasomnias refer to abnormalities of arousal, partial arousal, and transitions between stages of sleep. The second is an ultradian rhythm that occurs several times per night-the stages of sleep. Sleep stages cycle every 5060 minutes in infants to every 90 minutes in adolescents. The cues are light-dark, ambient temperature, core body temperature, noise, social interaction, hunger, pain, and hormone production. In the process of falling asleep, the individual enters stage 1, light sleep, characterized by reduced bodily movements, slow eye rolling, and sometimes opening and closing of the eyelids. Stage 2 sleep is characterized by slowing of eye movements, slowing of respirations and heart rate, and relaxation of the muscles but with repositioning of the body. Melatonin is a hormone that decreases core body temperature, which appears to play a role in sleep onset and sleep maintenance. Over the first year of life the infant slowly consolidates sleep at night into a 9- to 12-hour block and naps gradually decrease to one per day by about 12 months. Adolescents need 991/2 hours per night but often only get 771/4 hours per night.
The increasing number of males with eating disorders correlates with the increased media emphasis on muscular does kaiser cover erectile dysfunction drugs buy discount vardenafil 20 mg, chiseled appearance as the male ideal impotence quad hoc cheap 20 mg vardenafil overnight delivery. They present with more rapid weight loss and lower percentile body weight than adolescents icd 9 code erectile dysfunction neurogenic purchase vardenafil mastercard. When you look at yourself in the mirror, do you see yourself as overweight, underweight, or satisfactory? If your weight is satisfactory, has there been a time that you were worried about being overweight? Have you ever used nutritional supplements, diet pills, or laxatives to help you lose weight? In the restricting type, patients do not regularly engage in binge eating or purging. Distinguishing between the two is important as they carry different implications for prognosis and treatment. Refusal to maintain body weight at or above a minimally normal weight for age and height (eg, weight loss leading to maintenance of body weight less than 85% of that expected; or failure to make expected weight gain during a period of growth, leading to body weight less than 85% of that expected). In postmenarchal females, amenorrhea, ie, the absence of at least three menstrual cycles. Other diagnostic screening tools (eg, Eating Attitudes Test) assess a range of eating and dieting behaviors. Parental observations are critical in determining whether a patient has expressed dissatisfaction over body habitus and determining which weight loss techniques the child has used. If the teenager is unwilling to share his or her concerns about body image, the clinician may find clues to the diagnosis by carefully considering other presenting symptoms. Weight loss from a baseline of normal body weight is an obvious red flag and should raise the clinical suspicion for the presence of an eating disorder. Physical symptoms are usually secondary to weight loss and proportional to the degree of malnutrition. The body effectively goes into hibernation, becoming functionally hypothyroid (euthyroid sick) to save energy. Dizziness, lightheadedness, and syncope may occur as a result of orthostasis and hypotension secondary to impaired cardiac function. Left ventricular mass is decreased (as is the mass of all striated muscle), stroke volume is compromised, and peripheral resistance is increased, contributing to left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Inability to take in normal quantities of food, early satiety, and gastroesophageal reflux can develop as the body adapts to reduced intake. The normal gastrocolic reflex may be lost due to lack of stimulation by food, causing bloating and constipation. Neurologically, patients may experience decreased cognition, inability to concentrate, increased irritability, and depression, which may be related to structural brain changes and decreased cerebral blood flow. The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis shuts down as the body struggles to survive, directing finite energy resources to vital functions. This may be mediated by the effect of low serum leptin on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. Both males and females experience decreased libido and interruption of pubertal development, depending on the timing of the illness. Often patients eliminate fat from their diets and may eat as few as 100200 kcal/d. Patients tend to wear bulky clothes and may hide weights in their pockets or drink excessive fluid (waterloading) to trick the practitioner. The hypothalamic-pituitaryovarian axis shuts down under stress, causing hypothalamic amenorrhea. When weight loss is significant, adipose tissue is lost and there is not enough substrate to activate estrogen. Resumption of normal menses occurs only when both body weight and body fat increase. An adolescent female needs about 17% body fat to restart menses and 22% body fat if she has primary amenorrhea. One study demonstrated that target weight gain for return of menses is approximately 1 kg higher than the weight at which menses ceased. Bone densitometry should be done if amenorrhea has persisted for 6 months, as patients begin to accumulate risk for osteoporosis. Differential Diagnosis If the diagnosis is unclear (ie, the patient has lost a significant amount of weight but does not have typical body image distortion or fat phobia), then the clinician must consider the differential diagnosis for weight loss in adolescents.
These families might wish to bpa causes erectile dysfunction buy discount vardenafil 20 mg consider breast feeding and home child care for later children erectile dysfunction otc treatment discount vardenafil american express. The two viruses most clearly shown to erectile dysfunction icd 9 code purchase 20mg vardenafil amex precipitate otitis media are respiratory syncytial virus and influenza, accounting for the annual surge in otitis media cases from January to May in temperate climates. The clinical significance of this change is to decrease the overall percentage of drug-resistant pneumococci, since the serotypes included in the vaccine are the most multiply resistant. The fourth organism found is Streptococcus pyogenes, which is more common in school-aged children than in infants. The only difference is that the risk of gramnegative enteric infection is slightly increased in infants younger than age 4 weeks who are or have been hospitalized in a neonatal intensive care nursery. Microbiology of Acute Otitis Media the role of respiratory viral infection in precipitating otitis media is unquestionable, yet fewer than 12% of ear effusions culture positive for viruses. Recent studies with sensitive viral antigen or nucleic acid tests have detected virus in over 40% of infected ears. Disposable ear specula have become popular but are not needed for infection control, because reusable specula can be easily disinfected. The disposable specula are sharp at the tip and often cause pain when pushed to get an airtight seal. Cerumen removal-Cerumen removal is an essential skill for anyone who cares for children. Parents should be advised that ear wax protects the ear (cerumen contains lysozymes and immunoglobulins that inhibit infection) and usually comes out by itself; therefore, parents should never put anything solid into the ear canal to remove the ear wax. The physician may safely remove cerumen under direct visualization through the operating head of an otoscope, provided two adults are present to hold the child. After 20 minutes, irrigation with a soft bulb syringe can be started with water warmed to 3538°C to prevent vertigo. A good home remedy for recurrent cerumen impaction is a few drops of oil such as mineral or olive oil a couple of times a week warmed to body temperature to prevent dizziness. Tympanometry-Tympanometry can rapidly identify an effusion in infants over about 6 months, and it requires little training. It should be preceded by pneumatic otoscopy to assure that 50% or more of the canal is wax-free. Compliance is determined as air pressures are varied from +200 to 400 mm H2O in the sealed external ear canal. The height and sharpness of the peak is not important when using the Welch-Allyn tympanometer. Children with resistant strains tend to be younger and to have had more unresponsive infections. Antibiotic treatment in the preceding 3 months also increases the risk of harboring resistant pathogens. Penicillin resistance develops through stepwise mutations in the structure of the three penicillinbinding proteins. Strains for which minimum inhibitory concentrations of penicillin range between 0. Strains for which minimum inhibitory concentrations are equal to or higher than 2 mcg/mL are said to have "high-level resistance. Lower incidences are found in countries using fewer courses of antibiotic per person. Nationwide resistance rates include 63% for trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole, 32% for macrolides, and 2% for amoxicillin (dosed at 90 mg/kg/d). Oral cephalosporins vary widely in efficacy, with the highest resistance rates for cefixime and cefaclor and lowest rates (about 35%) for cefuroxime, cefprozil, cefpodoxime, and cefdinir. Over 90% of highly penicillin-resistant strains are still susceptible to clindamycin, rifampin, and fluoroquinolones. Fluoroquinolones are not yet approved for children younger than 16 years; however, studies are under way to assess their safety and efficacy in this age group. Contributing to errors in diagnosis are the temptation to accept the diagnosis without removing enough cerumen to adequately visualize the eardrum, and the mistaken belief that a red eardrum establishes the diagnosis. In fact, redness of the eardrum is often a vascular flush caused by fever, crying, or even efforts to remove cerumen.